How Much Does a Surrogate Make? A Comprehensive Guide for Intended Parents

Infertility is a heartbreaking reality for many couples around the world. Despite advancements in reproductive medicine, some couples are unable to conceive naturally or even with the help of treatments like Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) and In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). For these couples, alternative methods like surrogacy offer a viable path to parenthood. Gestational surrogacy, in particular, has become a popular choice, especially for couples with specific medical conditions, single parents, and LGBTQ+ couples.
One of the most common questions intended parents ask is, “How much does a surrogate make?” The compensation varies depending on the country and agency involved, but surrogate pay in the US typically ranges from $30,000 to $50,000.
- Book an online appointment: Get a free online consultation.
- Call\W:+91-8800481100 Email:neelam@ivfconceptions.com
If you are considering how surrogacy compensation works or wondering about average surrogate mother earnings, it’s essential to understand the financial aspects of the surrogacy process to ensure everything is properly planned.
But one of the most pressing questions parents often ask is, “How much does a surrogate make?” This guide provides a detailed breakdown of surrogate compensation, covering everything from base pay to additional allowances, and offers insights into how these payments are calculated.
More Resources to Read:
Surrogacy Guide for Surrogate Mothers
Surrogacy Guide for Intended Parents
How does the surrogacy process work
Understanding the Role of a Surrogate Mother
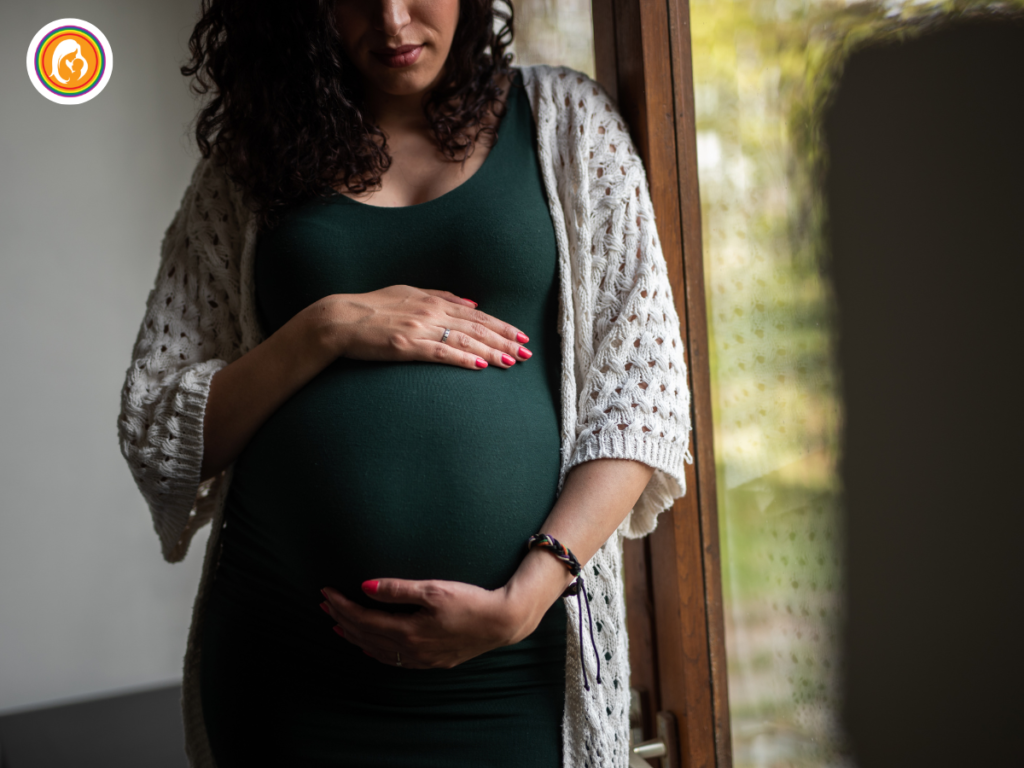

Before diving into the financial aspects, it’s essential to understand the crucial role a surrogate mother plays in the surrogacy process. A gestational surrogate, also known as a gestational carrier, carries a pregnancy for intended parents who are unable to do so themselves. Unlike traditional surrogacy, where the surrogate’s egg is used, gestational surrogacy involves implanting an embryo created using the intended parents’ or donors’ egg and sperm.
The surrogate has no genetic connection to the child she carries. Her role is purely to nurture the embryo into a healthy baby, providing a safe and supportive environment during pregnancy.
How Surrogate Mother Compensation is Calculated
The compensation a surrogate receives varies widely depending on several factors, including her location, experience, and the specific terms of the surrogacy agreement. Surrogacy compensation generally falls into three main categories: base compensation, surrogacy-related expenses, and additional allowances.
1. Base Compensation
Base compensation is the primary payment a surrogate receives from the intended parents. This payment compensates the surrogate for her time, effort, and the physical demands of carrying a pregnancy. The base compensation can vary significantly based on several factors:
- Experience: An experienced surrogate, who has successfully carried a surrogate pregnancy before, typically receives an additional $5,000 or more compared to a first-time surrogate. This is because experienced surrogates are often seen as lower risk, having already demonstrated their ability to carry a pregnancy to term.
- State of Residence: Compensation can also vary depending on where the surrogate lives. In surrogate-friendly states like California, where surrogacy laws are well-established and protective of all parties involved, surrogates tend to earn more. The high demand for surrogates in these states drives up compensation rates, often making California one of the highest-paying regions for surrogacy in the United States.
- Market Demand: The demand for surrogates can fluctuate based on various factors, including societal trends, legal changes, and international demand. In times of higher demand, surrogates may command higher base compensation.
Typically, base compensation for a first-time surrogate in the United States ranges from $35,000 to $50,000. This amount is usually paid in monthly installments, starting after the confirmation of a fetal heartbeat around six weeks into the pregnancy. Payments continue throughout the pregnancy and are managed by an escrow company to ensure the surrogate receives the agreed-upon amounts on time.
2. Coverage of Surrogacy-Related Costs
In addition to base compensation, intended parents are responsible for covering all expenses related to the surrogacy process. These expenses ensure that the surrogate does not incur any out-of-pocket costs while carrying the pregnancy. Key expenses include:
- Medical Costs: This includes all healthcare-related expenses, such as prenatal care, delivery, and any medical treatments required during the pregnancy. If the surrogate does not have insurance that covers surrogacy, the intended parents will need to purchase a suitable policy or cover all out-of-pocket expenses.
- Legal Costs: Surrogacy involves complex legal agreements to protect the rights of all parties involved. Intended parents cover the surrogate’s legal fees, including the cost of reviewing and negotiating the surrogacy contract. This ensures that the surrogate has independent legal representation throughout the process.
- Travel Expenses: If the surrogate needs to travel for medical appointments or embryo transfer procedures, the intended parents cover these costs. This includes airfare, lodging, car rentals, and meals during travel. Additionally, if the surrogate has children, the cost of childcare during her travels may also be covered.
- Insurance Premiums: Some surrogates may need specialized insurance plans that cover surrogacy-related medical care. Intended parents typically pay for these insurance premiums, ensuring the surrogate has access to the necessary healthcare services without financial strain.
3. Additional Compensation and Allowances
Beyond base compensation and covered expenses, surrogates may receive additional compensation for various circumstances that arise during the surrogacy journey. These additional payments recognize the potential risks and unexpected events that can occur during pregnancy. Examples include:
- Multiples (Twins or Triplets): Carrying multiples is more physically demanding and poses higher medical risks. Surrogates who carry twins or triplets typically receive an additional $5,000 to $10,000 for each additional child.
- C-Section Delivery: If a C-section is required, the surrogate may receive an additional fee, often ranging from $2,000 to $5,000, to compensate for the increased recovery time and potential complications associated with surgical delivery.
- Invasive Procedures: Surrogates may undergo additional medical procedures, such as amniocentesis or fetal reduction. These procedures can be physically and emotionally challenging, and surrogates may receive extra compensation ranging from $1,000 to $3,000 per procedure.
- Loss of Reproductive Organs: In the rare event that a surrogate loses reproductive organs due to complications during pregnancy or delivery, she may receive a significant compensation, often $5,000 to $10,000, to acknowledge the severity of such a loss.
- Maternity Clothing Allowance: Intended parents typically provide an allowance for maternity clothing, usually around $500 to $1,000, to ensure the surrogate is comfortable during her pregnancy.
- Breast Milk Pumping: Some intended parents request that the surrogate provide breast milk for the baby after birth. In such cases, the surrogate may receive compensation for the time and effort involved in pumping and storing the milk, often around $200 to $500 per week.
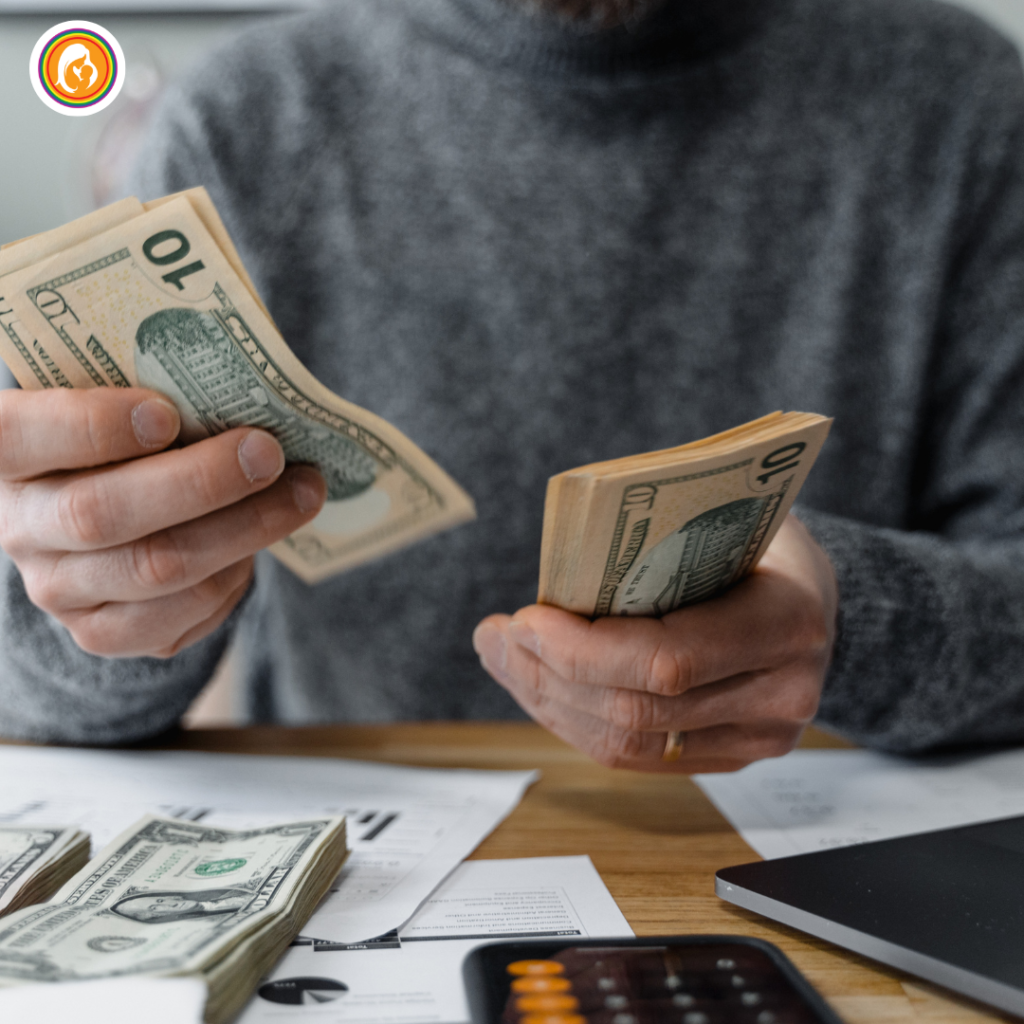

Comparing Surrogate Compensation Across Different Regions
Surrogate compensation varies not only within the United States but also internationally. The following table provides a comparison of average surrogate compensation in different regions:
| Region | Average Base Compensation | Additional Benefits |
| United States | $35,000 – $50,000 | Higher in surrogate-friendly states, additional fees for multiples, C-sections, etc. |
| Canada | $20,000 – $30,000 | Legal expenses covered, modest additional compensation for specific circumstances. |
| Ukraine | $15,000 – $25,000 | Surrogacy-friendly laws, additional allowances for travel and legal costs. |
| Georgia (Country) | $12,000 – $20,000 | Lower overall compensation, but full coverage of medical and travel expenses. |
| India (Pre-Ban) | $5,000 – $10,000 | Surrogacy now banned for foreigners, previously low compensation with minimal benefits. |
Additional guide for intended parents:
Best surrogacy agency in India
Best surrogacy agency in Mexico
Best surrogacy agency in Colombia
Best surrogacy agency in Argentina
Best surrogacy agency in Georgia
Conclusion: How to Navigate Surrogate Compensation
The compensation a surrogate receives is a crucial factor for both intended parents and surrogates themselves. However, it’s essential to remember that surrogacy is a deeply personal journey, involving not just financial considerations but also emotional, ethical, and legal complexities.
Intended parents should work closely with reputable surrogacy agencies and legal professionals to ensure that compensation agreements are fair, transparent, and tailored to the specific needs of their surrogacy journey. Additionally, prospective surrogates should thoroughly understand their compensation package, including how it addresses potential risks and unexpected events.
By understanding the various components of surrogate compensation, intended parents can make informed decisions that respect the surrogate’s contributions while also managing the financial aspects of their surrogacy journey.
If you’d like to learn more about IVF, Egg Donation, or surrogacy services globally, check out the rest of our website at Complete Surrogacy Agency. We offer legally secure and affordable surrogacy consulting services for FREE.
Complete Surrogacy: Your Trusted Partner in International Surrogacy
At Complete Surrogacy, we have over 15 years of experience in international surrogacy, guiding 4,000+ intended parents worldwide. We provide safe, ethical, and affordable surrogacy solutions for single parents, LGBTQ+ couples, and heterosexual couples.
As members of EFS and ESHRE, we adhere to the highest ethical and professional standards. Our expert team is committed to providing accurate, compassionate, and transparent guidance, ensuring a legally secure and smooth journey to parenthood.
Let us help you build your family with trust, care, and integrity.
Get in touch for one FREE Surrogacy Consultancy!

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Surrogate Compensation
1. How much does a surrogate make for her first surrogacy?
For a first-time surrogate in the United States, base compensation typically ranges from $35,000 to $50,000. The exact amount depends on factors such as the surrogate’s location and the demand for surrogates in that area.
2. Does a surrogate receive all of her compensation at once?
No, surrogate compensation is usually paid in installments throughout the pregnancy. Payments often begin after a fetal heartbeat is confirmed around six weeks and continue until the pregnancy is completed. An escrow company typically manages these payments to ensure they are made on time.
3. Are surrogates responsible for any costs during the surrogacy process?
No, intended parents cover all surrogacy-related costs, including medical expenses, legal fees, travel expenses, and insurance premiums. The surrogate should not incur any out-of-pocket expenses related to the pregnancy.
4. Can a surrogate receive additional compensation for carrying twins or triplets?
Yes, surrogates typically receive additional compensation if they carry multiples. This is due to the increased medical risks and physical demands associated with carrying more than one baby. The additional compensation usually ranges from $5,000 to $10,000 per additional child.
5. What happens if a surrogate has a C-section?
If a surrogate undergoes a C-section, she usually receives additional compensation, ranging from $2,000 to $5,000. This extra payment recognizes the extended recovery time and potential complications associated with surgical delivery.
6. Are surrogates compensated for unforeseen medical procedures during pregnancy?
Yes, surrogates may receive additional compensation for unexpected medical procedures, such as amniocentesis or fetal reduction. These payments acknowledge the physical and emotional challenges associated with such procedures.
7. Is there compensation for a surrogate who provides breast milk after delivery?
Some intended parents request that the surrogate provide breast milk for the baby after birth. In such cases, the surrogate may be compensated for the time and effort involved in pumping and storing the milk, typically around $200 to $500 per week.
8. Do surrogates receive compensation for maternity clothing?
Yes, intended parents usually provide a maternity clothing allowance, which typically ranges from $500 to $1,000. This allowance ensures that the surrogate can purchase comfortable clothing during her pregnancy.
9. How does the compensation differ between states in the U.S.?
Surrogate compensation can vary significantly depending on the state. For example, surrogates in California, a surrogate-friendly state with high demand, often receive higher compensation compared to surrogates in other states with less demand or more restrictive surrogacy laws.
10. What should intended parents consider when discussing compensation with a surrogate?
Intended parents should ensure that the compensation package is fair, transparent, and comprehensive. It should cover all potential costs and scenarios, including base compensation, additional allowances for medical procedures, and coverage of all surrogacy-related expenses. Working with a reputable surrogacy agency and legal professionals is crucial to navigating this process.
11. Can surrogates negotiate their compensation?
Yes, surrogates can negotiate their compensation with the intended parents, especially if they have specific needs or preferences. However, most compensation packages are standardized by surrogacy agencies to ensure fairness and transparency.
12. What is the role of an escrow account in surrogacy compensation?
An escrow account is used to manage the surrogate’s compensation. The intended parents deposit the agreed-upon funds into the escrow account, which is then managed by a third-party company. The escrow company ensures that payments are made on time and according to the terms of the surrogacy agreement.

Author Bio: Neelam Chhagani is an International Surrogacy Expert with 15 years of experience in the fertility and surrogacy domain. As the founder of IVF Conceptions and Complete Surrogacy, she has guided over 4,000 intended parents worldwide on their surrogacy journey to parenthood. Recognized as a trusted authority, she specializes in holistic infertility solutions and third-party reproduction consulting.
Holding an MA in Counselling Psychology and a PGD in Mental Health, Neelam is a proud member of the European Fertility Society (EFS) and the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). She is also a leading surrogacy blogger, providing valuable insights into ethical and practical surrogacy solutions.
Since 2010, committed to supporting ALL family types, Neelam has been passionate about helping intended parents grow their families with compassion, integrity, and a focus on secure and affordable surrogacy options Globally.
Learn more about Neelam:
https://www.ivfconceptions.com/neelam-chhagani-surrogacy-consultant/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/neelam-chhagani-92892229/














I was introduced to Neelam by a friend who worked with Neelam for surrogacy. Neelam is absolutely wonderful. I am a single male and the journey to fatherhood is not that easy. Neelam connected me to a program ideal for my circumstances. She was with me throughout the pregnancy providing advice and guidance along the way. I am so grateful I found her and am thrilled today that I have a beautiful daughter. I highly recommend Neelam to anyone who is on a journey to become a parent. Having a child has changed my world for the better. I wish others success with their own journey and recommend you connect with Neelam to find a path that is best for you.
SA (USA)