Who are Surrogate Mothers: Become A Surrogate Mother in 2025

Who are Surrogate Mothers: Become Surrogate Mother via Gestational Surrogacy.
Who are Surrogate Mothers? Surrogate mothers, also known as gestational carriers, are women who selflessly carry a baby for individuals or couples unable to conceive or sustain a pregnancy on their own. In gestational surrogacy, the surrogate has no genetic connection to the baby; instead, she carries an embryo created through IVF using the intended parents’ or donors’ genetic material. Surrogacy continues to evolve in 2025, offering hopeful parents a safe and ethical path to building their families. This incredible journey is a testament to compassion, trust, and medical advancements in reproductive technology.
- Book an online appointment: Get a free online consultation.
- Call\W:+91-8800481100 Email:neelam@ivfconceptions.com
In this comprehensive article, we delve into the world of surrogate mothers, answering your questions and shedding light on this noble endeavor.
Additional guide for intended parents:
Best surrogacy agency in India
Best surrogacy agency in Mexico
Best surrogacy agency in Colombia
Best surrogacy agency in Argentina
Best surrogacy agency in Georgia
Best surrogacy agency in the USA
Best surrogacy agency in Ukraine
Best surrogacy agency in Armenia
Key Takeaways
· A surrogate mother is a compassionate woman who chooses to carry and give birth to a child for the intended parents.
· They play a vital role in helping those struggling with infertility.
· Gestational surrogacy involves in vitro fertilization (IVF), with various combinations of genetic material.
· Surrogate mothers undergo rigorous screening to ensure their eligibility.
· The baby is not genetically related to the surrogate mother.
· Surrogacy can be gestational or traditional, with different methods and legal considerations.

Understanding Surrogate Mothers
Surrogate mothers are women who carry and give birth to a child on behalf of another person or couple. They offer hope to individuals or couples facing infertility challenges. Surrogate mothers are often motivated by a desire to help others experience the joy of parenthood. Some surrogates may also choose surrogacy as a means of financial support.
What is a surrogate mother?
A surrogate mother is a woman who carries and delivers a baby for another person or couple. She may be genetically related to the baby if she uses her own egg, or she may carry a baby created using the intended parents’ egg and sperm through in vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer.
How does surrogacy work?
Surrogacy is a process where a woman, the surrogate mother, agrees to carry a baby for another person or couple, the intended parents. It involves creating an embryo through IVF using the intended parents’ egg and sperm (or donor egg/sperm) and transferring it to the surrogate’s womb. The surrogate then carries the baby to term and delivers the child to the intended parents.
What is the difference between gestational surrogacy and traditional surrogacy?
Gestational surrogacy is when the surrogate mother carries a baby created using the intended parents’ egg and sperm or donor egg/sperm. The surrogate is not genetically related to the baby. In contrast, traditional surrogacy involves the use of the surrogate’s own egg, making her genetically related to the child she carries.
how do you become a surrogate mother?
If you are interested in becoming a surrogate mother, you can apply to a surrogacy agency. They will guide you through the surrogacy process, evaluate your eligibility based on surrogate mother requirements, and match you with intended parents who are looking for a surrogate.
What is the surrogacy journey like?
The surrogacy journey involves several steps. It starts with the application process and goes through medical and psychological screenings, legal contract negotiations, fertility treatments, embryo transfer, pregnancy, and ultimately, the delivery of the baby to the intended parents. It is a highly involved process that requires commitment and dedication from all parties involved.
What is the role of the surrogate mother in the surrogacy arrangement?
The surrogate mother is responsible for carrying and delivering the baby to the intended parents. She follows the medical protocols set by the fertility specialist and maintains open communication with the intended parents throughout the surrogacy journey. The surrogate’s well-being and the well-being of the baby are of utmost importance.
How is the surrogate mother compensated?
The compensation for surrogate mothers varies depending on various factors, including the surrogacy arrangement, geographical location, and individual circumstances. Typically, surrogate mothers receive financial compensation for their time.

Who Can Be a Surrogate Mother?
Surrogate mother requirements are essential to ensure a safe and successful surrogacy journey. Potential surrogate mothers should ideally be:
1. Aged 25 to 40: This age range is considered optimal for surrogate mothers.
2. Healthy and Physically Fit: Surrogate mothers should be in good physical health, with no underlying medical conditions.
3. Emotionally Stable: Emotional stability is crucial, given the emotional challenges involved in surrogacy.
4. Already a mother: Experience in childbirth is often preferred.
5. Motivated by the Desire to Help Others: Surrogate mothers should be genuinely committed to assisting intended parents in achieving their dream of parenthood.
These criteria ensure the well-being of both the surrogate mother and the future child. It’s important to note that surrogate mothers come from diverse backgrounds and are motivated by a variety of reasons, including the desire to give the gift of family to others and understand and fulfill Surrogate mother responsibilities.
Surrogacy Types: Gestational vs. Traditional
How does the surrogate mother get pregnant? Well, it depends on the type of surrogacy process. The surrogate mother gets pregnant via assisted reproductive technique (ART) like IVF with the intended mother’s eggs ( or egg donor) and the intended father’s sperm ( or sperm donor) and then embryos transfer to the surrogate mother.
Do surrogate mothers share blood with the baby? No, she does not in the case of the gestational surrogacy process.
Gestational Surrogacy
In gestational surrogacy, an embryo is created using the intended parent’s genetic material or donor material. This embryo is then transferred into the surrogate’s uterus. Importantly, the surrogate has no genetic relation to the baby, making this the most common surrogacy type in Australia.
Traditional Surrogacy
Traditional surrogacy involves the surrogate providing her own egg, which is fertilized with the intended father’s sperm. This can be achieved through artificial insemination or in vitro insemination (IVF). In this case, the baby is biologically related to the surrogate. It’s important to note that traditional surrogacy is not permitted in some Australian states.

Legal Aspects of Surrogacy
Surrogacy laws vary from country to country and from state to state, with each jurisdiction having its own regulations. It’s essential to understand these legal aspects before embarking on a surrogacy journey.
Legal processes, such as formal surrogacy agreements, eligibility requirements, and parentage orders, must be adhered to and need to be discussed with your legal team or surrogacy agency professional. The surrogate mother’s legal rights and responsibilities are well documented in the surrogacy agreement.
How does the Surrogacy Process Work?
Whose eggs are used in surrogacy? It is mostly intended for mother or female-parent eggs used in the surrogacy process. However, in some cases, when the female is in a higher age group, has low AMH, has some genetic issues, or has some health issues, then she can use an egg donor. This is known as egg donor surrogacy and in this case, egg donor eggs and father sperm are used.
Surrogacy typically involves in vitro fertilization (IVF), where an embryo is created through various combinations, such as:
1. Intended Parents’ Sperm and Egg: This involves using both the genetic material of the intended parents.
2. Donor Egg and Intended Father’s Sperm: In cases where the intended mother may have difficulty conceiving with her own eggs, a donor egg is used.
3. Donor Sperm and Intended Mother’s Egg: When the intended mother’s eggs are viable but the sperm is the concern, donor sperm is utilized.
4. Donor Sperm and Egg: In some instances, both the egg and sperm are donated.
5. Donor Embryo: Occasionally, embryos donated by individuals who have undergone IVF procedures are used.
The selected sperm/egg combination is then implanted into the surrogate mother via IVF. This crucial step ensures that the baby will not be genetically related to the surrogate mother.
Why do Women Become Surrogate Mother
The role of the surrogate mother is more than just carrying a baby for financial gain as it is a more emotionally bonding process. Surrogate mothers are motivated by a variety of reasons. While financial compensation can be a factor, most surrogacy mothers are primarily driven by their desire to bring joy and fulfillment to a deserving family.
Many of them find immense satisfaction in the pregnancy journey and the knowledge that they are helping others realize their dreams of parenthood.
Becoming a surrogate mother is a remarkable and selfless decision. If you’re considering this path, it’s crucial to understand the emotional and legal aspects involved. Surrogate mothers have rights, including financial compensation for pregnancy-related expenses. Communication and understanding between surrogate mothers and intended parents are key to a successful surrogacy journey.
Emotional Aspects of Surrogacy
Surrogacy can be emotionally challenging, both for surrogate mothers and intended parents. It’s vital for all parties involved to receive emotional support and counseling throughout the process. Open and honest communication is essential to navigate the emotional aspects of surrogacy successfully.
Role of Surrogacy Agencies
Surrogate mother agencies play a vital role in the surrogacy process. They can help match intended parents with suitable surrogate mothers, provide legal guidance, and offer emotional support. Finding a reputable surrogacy agency is essential for a smooth journey.
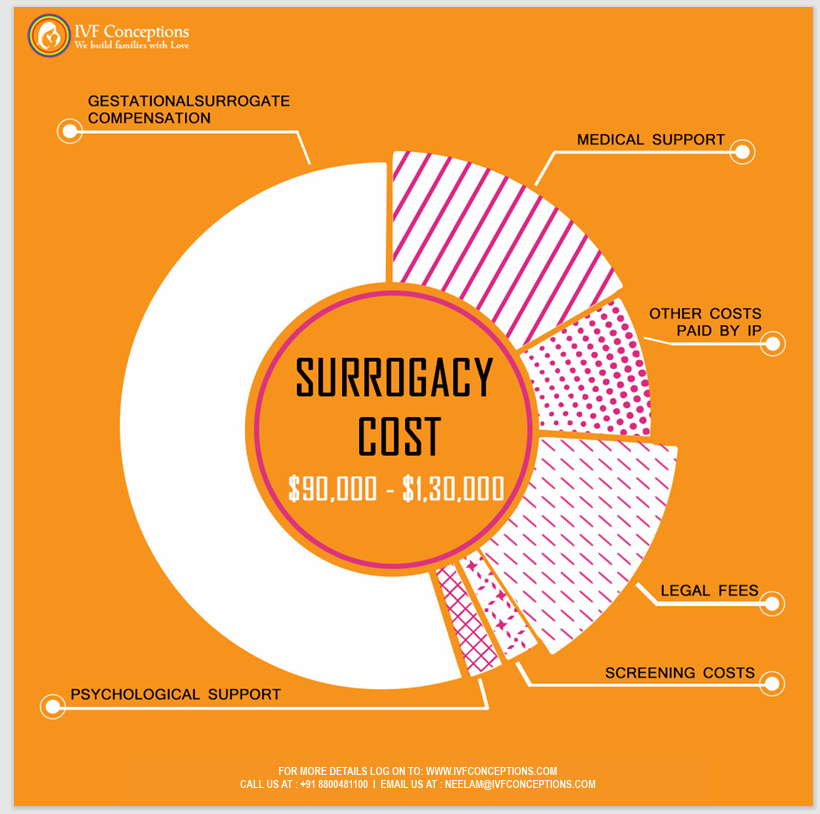
Surrogacy Cost and Surrogate Mother Compensation
Surrogate mother costs vary widely based on factors such as location and agency fees. Average surrogate mother compensation typically ranges from $30,000 to $50,000. Additional expenses include medical, legal, and insurance costs.
Breaking Down Surrogate Mother Cost
1. Surrogate Compensation
o Surrogate mother compensation varies based on location and agency fees.
o On average, surrogates can earn between $30,000 to $50,000 for their services.
2. Medical Expenses
o Medical expenses cover prenatal care, fertility treatments, and delivery.
o Intended parents typically cover these costs, and they can range from $20,000 to $30,000.
3. Legal Fees
o Legal contracts are essential in surrogacy and involve legal fees.
o Legal fees can vary but usually fall within the range of $5,000 to $10,000.
Additional Surrogacy Costs
1. Insurance
o Surrogate mothers should have comprehensive health insurance.
o Insurance costs can vary depending on the surrogate’s existing coverage and needs.
2. Agency Fees
o If you’re working with a surrogacy agency, there will be agency fees.
o These fees cover the matching process, support, and coordination throughout the journey.
3. Travel Expenses
o If the surrogate lives in a different location than the intended parents, travel expenses may be necessary.
o These costs can include flights, accommodations, and meals.

Becoming a Surrogate Mother
Requirements for Gestational Surrogate Mothers
Women who consider becoming surrogate mothers must meet certain criteria. These requirements often include:
- A strong desire to help others fulfill their dreams of parenthood.
- Good physical and mental health, as assessed through a screening process.
- A willingness to adhere to a legal contract that outlines the terms and expectations of the surrogacy arrangement.
- A commitment to a healthy lifestyle to ensure a successful pregnancy and delivery.
The Process of surrogacy
The surrogacy journey involves several essential steps:
1. Application: Those interested in becoming a surrogate mother typically start by applying through a surrogacy agency.
2. Screening Process: Applicants undergo thorough physical and psychological evaluations to ensure they are fit for surrogacy.
3. Matching Process: Once accepted, the surrogate is matched with intended parents who share common goals and values.
4. Embryo Transfer: In gestational surrogacy, the embryo created from the intended parents’ egg and sperm is transferred into the surrogate’s womb.
5. Pregnancy and Birth: The surrogate carries the pregnancy and gives birth to the child.
6. Parental Rights: Upon birth, the intended parents typically assume parental rights, and the surrogate has no genetic or legal ties to the child.
Compensation and Legal Aspects
Surrogate mothers are compensated for their time and effort, although the specifics can vary. Compensation is often determined using a surrogate pay calculator. Legal contracts are crucial to protect the rights and responsibilities of all parties involved.
More Resources to Read:
Surrogacy with Own Eggs
Guaranteed Surrogacy Programs
Surrogacy for HIV +ve IPs
Surrogacy For Single Parent
Conclusion
Surrogate mothers are unsung heroes in the world of reproductive health. Their selflessness changes lives, allowing individuals and couples to realize their dream of parenthood. As surrogacy continues to evolve with advancements in medical technology and changes in legal frameworks, the role of surrogate mothers will remain crucial in this journey toward parenthood.
Whether you are considering becoming a surrogate mother or are intended parents exploring this option, it’s essential to be well-informed about the process, legal aspects, and emotional challenges. With the right support and knowledge, surrogacy can bring the gift of parenthood to those who dream of it.
If you’d like to learn more about IVF, Egg Donation, or surrogacy services globally, check out the rest of our website at Complete Surrogacy Agency. We offer legally secure and affordable surrogacy consulting services for FREE.
For more resources on IVF and Surrogacy, browse our other web page- IVF Conceptions.
For more resources on IVF and Surrogacy, browse our other web page- Georgia Surrogacy Agency.
Complete Surrogacy: Your Trusted Partner in International Surrogacy
At Complete Surrogacy, we have over 15 years of experience in international surrogacy, guiding 4,000+ intended parents worldwide. We provide safe, ethical, and affordable surrogacy solutions for single parents, LGBTQ+ couples, and heterosexual couples.
As members of EFS and ESHRE, we adhere to the highest ethical and professional standards. Our expert team is committed to providing accurate, compassionate, and transparent guidance, ensuring a legally secure and smooth journey to parenthood.
Let us help you build your family with trust, care, and integrity.
Get in touch for one FREE Surrogacy Consultancy!
Our team includes experts from diverse backgrounds with leading reproductive attorneys, professionally trained top fertility doctors, former surrogacy case managers, experienced and kind surrogate mother and egg donor coordinators, mental health professionals specializing in infertility counseling, and a logistic support team to assist you in your chosen surrogacy country.
FAQs For Who Are Surrogate Mothers?
Who is the biological mother of a surrogate child?
The biological mother of a surrogate child is not the surrogate mother. It is either the intended mother (genetic mother) or a donor, depending on the type of surrogacy.
How does a surrogate mother get pregnant?
A surrogate mother gets pregnant through in vitro fertilization (IVF), where an embryo is created outside her body and then implanted into her uterus. In the case of traditional surrogacy, an artificial insemination process might be used.
Who owns the baby of a surrogate mother?
The baby of a surrogate mother is typically owned by the intended parents legally and genetically, as they provide either the genetic material or donor material for conception. They are known as commissioning parents.
Does a surrogate mother share DNA with the baby?
No, a surrogate mother does not share DNA with the baby if it’s gestational surrogacy, as the baby’s genetics come from the intended parents or donors. In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate may share genetic material with the baby.
What is the role of a surrogate mother?
The role of a surrogate mother is to carry and give birth to a child for the intended parents. She provides a safe environment for pregnancy and childbirth.
How does surrogacy work?
Surrogacy typically involves in vitro fertilization (IVF), where an embryo is created using the intended parents’ or donor’s genetic material and then implanted in the surrogate’s uterus for gestation.
Are there different types of surrogacy?
There are two main types of surrogacy: gestational surrogacy, where the surrogate has no genetic connection to the baby, and traditional surrogacy, where the surrogate contributes her own egg.
What are the legal aspects of surrogacy?
The legal aspects of surrogacy vary by location. It often involves legal agreements, parental rights, and compliance with local surrogacy laws.
How are surrogate mothers compensated?
Surrogate mothers are compensated for their time, effort, and medical expenses. Compensation rates vary and depend on various factors.
Can a relative be a surrogate mother?
Yes, in some cases, a relative can be a surrogate mother if both parties agree and meet legal and medical requirements.
What are the emotional aspects of surrogacy?
Surrogacy can involve complex emotional challenges for all parties involved, including the surrogate, intended parents, and the child. Emotional support is essential.
Are there medical criteria for surrogate mothers?
Yes, there are typically medical criteria for surrogate mothers, including good physical and mental health, prior successful pregnancies, and a supportive network.
What are the risks involved in surrogacy?
Risks in surrogacy can include medical complications, legal issues, and emotional challenges. It’s important to be aware of and mitigate these risks.
How long does the surrogacy process take?
The duration of the surrogacy process varies, but it can take several months to over a year from the initial preparations to the birth of the child. In general, we can say it takes 15 to 24 months to complete the full surrogacy process successfully.
Reference used:

Author Bio: Neelam Chhagani is an International Surrogacy Expert with 15 years of experience in the fertility and surrogacy domain. As the founder of IVF Conceptions and Complete Surrogacy, she has guided over 4,000 intended parents worldwide on their surrogacy journey to parenthood. Recognized as a trusted authority, she specializes in holistic infertility solutions and third-party reproduction consulting.
Holding an MA in Counselling Psychology and a PGD in Mental Health, Neelam is a proud member of the European Fertility Society (EFS) and the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). She is also a leading surrogacy blogger, providing valuable insights into ethical and practical surrogacy solutions.
Since 2010, committed to supporting ALL family types, Neelam has been passionate about helping intended parents grow their families with compassion, integrity, and a focus on secure and affordable surrogacy options Globally.
Learn more about Neelam:
https://www.ivfconceptions.com/neelam-chhagani-surrogacy-consultant/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/neelam-chhagani-92892229/














I was introduced to Neelam by a friend who worked with Neelam for surrogacy. Neelam is absolutely wonderful. I am a single male and the journey to fatherhood is not that easy. Neelam connected me to a program ideal for my circumstances. She was with me throughout the pregnancy providing advice and guidance along the way. I am so grateful I found her and am thrilled today that I have a beautiful daughter. I highly recommend Neelam to anyone who is on a journey to become a parent. Having a child has changed my world for the better. I wish others success with their own journey and recommend you connect with Neelam to find a path that is best for you.
SA (USA)