Surrogacy Definition and Surrogacy Meaning: Understanding the Process
Are you curious about how surrogacy can change the path to parenthood? It’s a complex option for building a family. A woman, known as a surrogate or gestational carrier, carries and delivers a child for another person or couple, called the intended parents. This process involves many parts, like surrogate motherhood and the types of surrogacy.
Medical professionals, legal experts, and others play big roles in the surrogacy journey. They help make sure the process is successful and healthy. Understanding the surrogacy definition and its meaning is crucial for those considering this path.
- Book an online appointment: Get a free online consultation.
- Call\W:+91-8800481100 Email:neelam@ivfconceptions.com
The laws about surrogacy vary by state, adding to the complexity. But knowing the surrogacy process and its meaning can help you achieve your dream of becoming a parent. From gestational surrogacy to understanding the legal aspects of surrogacy, this guide will help you navigate the path to parenthood.
Key Takeaways
- Most pregnancies through gestational surrogacy rely on in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Gestational surrogacy is the prevalent type, while traditional surrogacy is illegal in many states.
- An ideal gestational carrier is between 21 and 45 years old and has a healthy pregnancy history.
- Legal contracts are crucial and must be established before beginning the IVF process.
- Surrogacy costs can range from $50,000 to over $150,000, influenced by various factors.
- Approximately 750 babies are born via gestational surrogacy in the U.S. each year.
- Understanding surrogacy laws is vital, as they differ significantly from state to state.
More Resources to Read:
Infertility Treatment and Surrogacy Process
9 Factors To Improve IVF Pregnancy Rate
International Surrogacy Options Worldwide
Surrogacy Guide for Surrogate Mothers
What is Surrogacy and what does surrogacy mean?
Surrogacy is a way for people or couples to become parents when they can’t conceive naturally. It includes different methods, each with its own process and meaning. Knowing what surrogacy is is key for those thinking about it.
Surrogacy Definition and surrogacy meaning Explained
Surrogacy means a woman agrees to carry and give birth to a child for someone else. It’s important for those facing fertility issues or other challenges. It’s more than a deal; it’s about building meaningful connections.

Types of Surrogacy: Traditional vs. Gestational
There are two main types of surrogacy: traditional and gestational. Each has its own features and effects on those involved.
| Type of Surrogacy | Description | Genetic Relation |
| Traditional Surrogacy | The surrogate is artificially inseminated with the father’s sperm. She is the biological mother of the child. | Surrogate is the biological mother. |
| Gestational Surrogacy | Involves IVF to create an embryo using eggs and sperm from the intended parents or donors; the surrogate carries the child but has no genetic link. | No genetic relation to the surrogate. |
Gestational surrogacy is more common in the U.S. because it’s legally clear. It lets intended parents, including same-sex couples, have a genetically related child. They also get to build a supportive bond with the gestational carrier.
Knowing the difference between traditional and gestational surrogacy is crucial. It affects how intended parents and surrogates prepare and participate in the process. Each type needs careful thought about the emotional, legal, and medical sides.
Understanding the Surrogacy Process
The surrogacy process is a detailed journey for the intended parents and the surrogate mother. It involves several key steps. Knowing each phase and the roles of everyone involved is important for a smooth experience. This guide aims to help you understand what to expect on this life-changing journey.
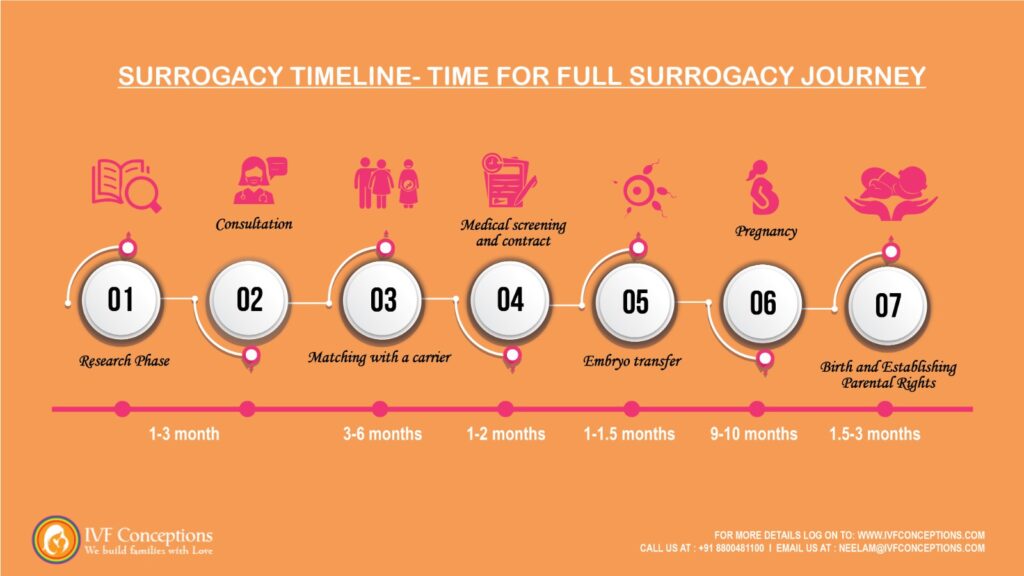
The surrogacy process takes 18 months to 24 months depending upon the individual circumstances
Outlines the surrogacy process timeline for intended parents:
| Stage | Description of Stage | Duration |
| Research Phase | Explore family building options and decide on surrogacy. | Personal timeframe |
| Consultation and Application | Choose a surrogacy agency, sign agreement, and start embryo creation (if needed). | 1-3 Months |
| Matching | Agency finds and presents potential gestational carriers. Meet and decide on a match. | 3-6 Months |
| Medical Screening and Contracts | Carrier undergoes medical and psychological screening. Sign surrogacy contract. | 1-2 Months |
| Embryo Transfer | Prepare for embryo transfer. Success may take multiple attempts. | 1-1.5 Months |
| Pregnancy | Gestational carrier’s pregnancy, approximately 40 weeks. | 9-10 Months |
| Birth and Postpartum | Baby’s birth, establish parental rights, and postpartum period. | 1.5-3 Months |
Please keep in mind that the durations mentioned in the table are approximate and can vary depending on individual circumstances and other factors. Always consult with a reputable surrogacy agency or professional to get personalized guidance throughout the surrogacy journey.
Overview of Steps in Surrogacy
The surrogacy process includes several main steps:
- Initial Consultation: Intended parents and a surrogacy agency talk about their needs and hopes.
- Surrogate Selection: Intended parents pick a qualified surrogate mother.
- Medical Evaluation: The surrogate’s health is checked to make sure she’s a good match.
- Legal Contracts: Detailed legal agreements are made to protect everyone involved.
- Fertilization Process: Medical steps like IVF are done to help the pregnancy start.
- Monitoring Pregnancy: Regular check-ups are done to keep the surrogate and fetus healthy.
- Delivery: The surrogate gives birth, and the child’s parents’ rights are transferred.
Key Parties Involved in Surrogacy
Several important people and groups play big roles in surrogacy:>
- Intended Parents: Those wanting to have a child through surrogacy.
- Surrogate Mother: The woman who carries the pregnancy, either as a gestational surrogate or a traditional surrogate.
- Fertility Specialists: Medical experts who look after the health and pregnancy.
- Surrogacy Agencies: Groups that help connect intended parents with surrogates.
- Legal Professionals: Lawyers who handle the legal side of surrogacy agreements and parental rights.
| Party | Role | Responsibility |
| Intended Parents | Seek assistance in having a child | Funding, support, and legal compliance |
| Surrogate Mother | Gestational carrier | Carrying the child, making health decisions |
| Fertility Specialists | Health care provider | Oversee IVF or IUI procedures |
| Surrogacy Agencies | Facilitator | Connects intended parents with surrogates |
| Legal Professionals | Advisor | Draft and review contracts, ensure legal protection |
Going through the surrogacy process needs teamwork from all involved. Knowing everyone’s roles and responsibilities makes the journey better. It also protects the interests of both the intended parents and the surrogate mother.
Surrogacy Definition: Types and Methods
There are different types of surrogacy, each with its own process. The main types are gestational surrogacy and traditional surrogacy. Knowing about these can help you understand your options better.
Gestational Surrogacy
Gestational surrogacy is the more common and preferred choice. It involves creating an embryo through IVF and implanting it in the surrogate. The surrogate doesn’t share genetic ties with the child, as the embryo comes from the intended parents or donors.
This method uses advanced medical technologies to increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Traditional Surrogacy
Traditional surrogacy, on the other hand, involves the surrogate’s own eggs and the intended father’s sperm. This makes the surrogate the biological mother of the child. Though it’s less common today, it’s still an option for families looking for alternative ways to become parents.
Medical Technologies Used in Surrogacy
Modern medical technologies are key in both types of surrogacy. IVF helps in selecting and transferring embryos, boosting success rates. The choice between fresh or frozen embryo transfers depends on the situation.
Both methods require careful medical monitoring and preparation. The surrogate needs hormone treatments, like estrogen and progesterone, to support a healthy pregnancy.
| Type of Surrogacy | Genetic Connection | Common Medical Technologies |
| Gestational Surrogacy | No | In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Embryo Transfer |
| Traditional Surrogacy | Yes | Artificial Insemination |
Legal Aspects of Surrogacy
Surrogacy’s legal side is key to a smooth journey. Knowing your state’s laws is crucial. These laws shape your rights and duties as parents and surrogates. Different states have their own rules, which can affect contract validity.
Navigating Surrogacy Laws in the U.S.
Surrogacy laws vary across the U.S. California is very open to surrogacy, making it easy for parents to be recognized. Arizona, however, bans surrogacy, limiting options for those who want this path. Knowing these differences is vital for intended parents to follow local laws.
Importance of Legal Contracts
Legal contracts are essential in surrogacy. They outline everyone’s rights and duties, including payment and medical care. Without clear contracts, misunderstandings can arise. It’s important to have a lawyer who knows surrogacy laws to make sure contracts are valid.

Parental Rights and Responsibilities
Getting parental rights is a big part of surrogacy. States like Arkansas and Alabama allow pre-birth orders but have rules. Some states only let one parent be recognized before birth, needing more legal steps after. Clear rights protect parents and surrogates from future legal issues.
| State | Surrogacy Type | Parental Rights |
| California | Gestational & Traditional | Recognized at birth |
| Texas | Gestational only | Validations required by court |
| Arizona | Prohibited | Not applicable |
| Alabama | Gestational | Pre-birth orders for married couples or single genetic parents |
| New York | Gestational | Clear guidelines for agreements, recognized post-birth |
Cost of Surrogacy: What to Expect
Surrogacy can be a costly journey. It’s important for intended parents to know the costs. These include agency fees, medical bills, legal fees, and payments to the surrogate. Costs can range from $70,000 to $230,000.
Breaking Down Surrogacy Costs
Here’s a detailed look at surrogacy costs:
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost Range |
| Surrogacy Agency Fees | $15,000 – $30,000 |
| Legal Fees | $3,000 – $15,500 |
| Surrogate Compensation | $43,700 – $86,900 |
| Medical and IVF Costs | $12,000 – $17,000 |
| Screening Costs | $0 – $4,000 |
| Insurance Costs | $4,300 – $28,300 |
| Other Miscellaneous Costs | $13,500 – $19,900 |
Factors Affecting the Price
Several factors can affect surrogacy costs. Consider these:
- Geographical Location: Costs can change based on where you are due to agency prices and living costs.
- Experience of the Surrogate: More experienced surrogates may ask for more money.
- Medical Needs: Extra medical procedures can increase costs.
- Length of the Journey: A longer journey means more costs for medical and legal services.
Understanding surrogacy costs is key for a smooth journey. As the surrogacy industry grows, it’s vital for parents to stay informed and flexible about costs from different agencies.
Cheapest countries for surrogacy:
| Country | Regulation & Organization | Who are allowed to participate | Surrogacy Cost | Legal Assurance |
| Colombia | Altruistic | Singles, gay couples, hetero couples | Affordable$70,000 | Reliable |
| Mexico | Altruistic | Singles, gay couples, hetero couples | Affordable$70,000 to $80,000 | Reliable |
| USA | Commercial | Singles, gay couples, hetero couples | Costly$150,000+ | Strong |
| Ukraine | Commercial | Hetero couples | Affordable$60,000 | Strong |
| Georgia | Commercial | Hetero couples | Affordable$60,000 | Strong |
| Greece | Altruistic | Hetero couples and single women | Affordable$80,000 | Strong |
Advantages and Risks of Surrogacy
Surrogacy can change lives for those wanting to start a family. It’s key to know the surrogacy advantages and risks. This helps in making a smart choice. Surrogacy can lead to parenthood, but it’s important to think it through carefully.
Surrogacy Advantages for Intended Parents
Many find surrogacy offers unique experiences. Key benefits include:
- Genetic Connection: Intended parents can have a genetic link to their child, especially in gestational surrogacy.
- Elimination of Pregnancy Risks: It’s a way to avoid pregnancy risks for those with health concerns.
- Higher Success Rates: Surrogates often have high success rates, making it a favorable option.
- Support from a Surrogate Agency: A good agency offers help and resources, making the journey smoother.
Surrogacy Risks to Consider
There are also risks to think about. These include:
- Financial Commitments: Surrogacy can be expensive, with costs for legal, medical, and surrogate compensation.
- Emotional Challenges: The journey can bring up feelings of anxiety and uncertainty for all involved.
- Time Investment: The whole process can take over a year, requiring a big time commitment.
- Legal Complexities: The legal side needs careful attention to ensure everyone’s rights are protected.
Talking openly about risks and benefits helps make informed choices. Working with a reliable surrogate agency can offer more insights and prepare you for this rewarding journey.
International surrogacy counties
Sure, here’s the information on international surrogacy laws organized in a table format:
| Country | Eligibility for Surrogacy | Types of Surrogacy Allowed | Legal Protection for Intended Parents | Accessibility for Foreigners | Advertising for Surrogates |
| Australia | Altruistic surrogacy only | No donor or surrogate matching | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not legal |
| Canada | Altruistic surrogacy only | Not applicable | Not applicable | Altruistic surrogacy allowed | Not applicable |
| Greece | Heterosexual couples, single females | Not applicable | Not applicable | Foreign nationals allowed | Not applicable |
| Georgia | Heterosexual couples (including foreigners) | Compensated surrogacy | Well protected | Foreigners allowed | Not applicable |
| Ukraine | Heterosexual couples (including foreigners) | Compensated surrogacy | Well protected | Foreigners allowed | Not applicable |
| India | Indian citizens only | Commercial surrogacy allowed | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Israel | Heterosexual Israeli citizens | Altruistic surrogacy only | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Kenya | Locals and foreigners | Compensated surrogacy | Not legally protected | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Laos | Foreigners only | Compensated surrogacy | Not legally protected | Foreigners allowed | Not applicable |
| Nigeria | Heterosexual Nigerian citizens | Altruistic and commercial surrogacy | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| South Africa | Heterosexual South African residents | Altruistic surrogacy | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| Thailand | Heterosexual Thai couples | Altruistic surrogacy only | Not applicable | Not applicable | Not applicable |
| UK | Not applicable | Altruistic surrogacy only | Not applicable | Foreigners cannot access | Not legal |
| USA | Gay and heterosexual foreigners | All forms of surrogacy | Well regulated | Foreigners allowed | Not applicable |
More Resources to Read:
Surrogacy Guide for Surrogate Mothers
Surrogacy Guide for Intended Parents
How does the surrogacy process work
Conclusion
Understanding surrogacy is key for those thinking about it as a way to become parents. It offers a path for building families when other ways are not possible. With the help of agencies, lawyers, and medical teams, the journey can be smoother.
As surrogacy becomes more common, knowing its legal, financial, and emotional sides is crucial. Costs, laws, and ethics are important to consider. Getting advice from experts in surrogacy can help you make good choices.
Surrogacy is more than just contracts and medical steps. It touches on the social and emotional sides of creating a family. Starting this journey can change your life in big ways. Being well-informed can help you face each step with confidence. Take the first steps towards your dream of becoming a parent through surrogacy.
If you’d like to learn more about IVF, Egg Donation, or surrogacy services globally, check out the rest of our website at Complete Surrogacy Agency. We offer legally secure and affordable surrogacy consulting services for FREE.
Complete Surrogacy: Your Trusted Partner in International Surrogacy
At Complete Surrogacy, we have over 15 years of experience in international surrogacy, guiding 4,000+ intended parents worldwide. We provide safe, ethical, and affordable surrogacy solutions for single parents, LGBTQ+ couples, and heterosexual couples.
As members of EFS and ESHRE, we adhere to the highest ethical and professional standards. Our expert team is committed to providing accurate, compassionate, and transparent guidance, ensuring a legally secure and smooth journey to parenthood.
Let us help you build your family with trust, care, and integrity.
Get in touch for one FREE Surrogacy Consultancy!

FAQ for what is the meaning of surrogacy and surrogacy defination
What is the definition of surrogacy?
Surrogacy is when a woman, called a surrogate, carries a child for someone else. This person or couple is called the intended parents.
What are the different types of surrogacy?
There are two main types. Traditional surrogacy means the surrogate is artificially inseminated and is the child’s biological mother. Gestational surrogacy uses IVF, so the surrogate isn’t genetically related to the child.
What does the surrogacy process generally involve?
The process starts with choosing a surrogate. Then, medical checks and legal contracts are signed. Next, fertilization happens, and the surrogate prepares for pregnancy. The journey continues with monitoring until the baby is born.
Who are the key parties involved in a surrogacy arrangement?
Key people include the surrogate, the intended parents, and fertility experts. Surrogacy agencies and lawyers also play important roles. They make sure everyone’s rights are respected.
How does gestational surrogacy work?
In gestational surrogacy, an embryo is made through IVF. It uses the intended parents’ or donors’ eggs and sperm. The surrogate carries and delivers the baby, with no biological link to it.
What are the legal aspects surrounding surrogacy?
Surrogacy laws vary by state. They require legally binding contracts. These contracts outline everyone’s rights and responsibilities. They’re key to avoiding legal issues.
What are the typical costs associated with surrogacy?
Surrogacy costs can be high, from $50,000 to $150,000 or more. This includes agency fees, medical bills, legal costs, and the surrogate’s compensation. Costs can change based on location and the surrogate’s experience.
What advantages does surrogacy offer intended parents?
Surrogacy lets intended parents have a genetically related child. It also allows them to experience parenthood, especially when natural conception isn’t possible.
What risks should intended parents consider before pursuing surrogacy?
Surrogacy comes with emotional, financial, and medical risks. These risks affect both the intended parents and the surrogate. It’s crucial for parents to understand these risks before starting.
Source Links
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/23186-gestational-surrogacy – Gestational Surrogacy: What Is It, Process, Risks & Benefits
- https://www.webmd.com/infertility-and-reproduction/using-surrogate-mother – What Is Surrogacy and How Does It Work?
- https://tdlawgroup.com/home/surrogacy-and-assisted-reproduction/surrogacy-information/surrogacy-meaning/ – What Does Surrogacy Mean?
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Surrogacy – Surrogacy

Author Bio: Neelam Chhagani is an International Surrogacy Expert with 15 years of experience in the fertility and surrogacy domain. As the founder of IVF Conceptions and Complete Surrogacy, she has guided over 4,000 intended parents worldwide on their surrogacy journey to parenthood. Recognized as a trusted authority, she specializes in holistic infertility solutions and third-party reproduction consulting.
Holding an MA in Counselling Psychology and a PGD in Mental Health, Neelam is a proud member of the European Fertility Society (EFS) and the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). She is also a leading surrogacy blogger, providing valuable insights into ethical and practical surrogacy solutions.
Since 2010, committed to supporting ALL family types, Neelam has been passionate about helping intended parents grow their families with compassion, integrity, and a focus on secure and affordable surrogacy options Globally.
Learn more about Neelam:
https://www.ivfconceptions.com/neelam-chhagani-surrogacy-consultant/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/neelam-chhagani-92892229/














I was introduced to Neelam by a friend who worked with Neelam for surrogacy. Neelam is absolutely wonderful. I am a single male and the journey to fatherhood is not that easy. Neelam connected me to a program ideal for my circumstances. She was with me throughout the pregnancy providing advice and guidance along the way. I am so grateful I found her and am thrilled today that I have a beautiful daughter. I highly recommend Neelam to anyone who is on a journey to become a parent. Having a child has changed my world for the better. I wish others success with their own journey and recommend you connect with Neelam to find a path that is best for you.
SA (USA)