ART Cryopreservation: What Is It and How Does It Work?

ART Cryopreservation: What Is It and How Does It Work?
ART Cryopreservation has emerged as a crucial technology in Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART), offering individuals and couples the flexibility to preserve their fertility for future use. This process involves freezing embryos, eggs, or sperm using advanced techniques like vitrification to maintain their viability for years.
- Book an online appointment: Get a free online consultation.
- Call\W:+91-8800481100 Email:neelam@ivfconceptions.com
By choosing ART Cryopreservation, intended parents can safeguard their reproductive options, whether due to medical conditions, delayed family planning, or fertility preservation before cancer treatment. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of cryopreservation in ART, how it works, and its various applications, helping you make informed decisions about your fertility journey.
What Is Cryopreservation?
Cryopreservation refers to the process of freezing biological samples such as cells, tissues, or organs at extremely low temperatures, typically between -80°C and -196°C, to halt cellular activity and preserve them for future use. In the context of ART, cryopreservation plays a vital role in storing reproductive cells—sperm, eggs, and embryos—allowing for flexibility in family planning.
More Resources to Read:
Infertility Treatment and Surrogacy Process
9 Factors To Improve IVF Pregnancy Rate
International Surrogacy Options Worldwide
Surrogacy Guide for Surrogate Mothers
Key Concepts:
- Cryoprotectants: These are special chemicals used to protect cells from ice crystal damage during the freezing process.
- Vitrification: A rapid freezing technique that prevents the formation of ice crystals, making it particularly effective for preserving eggs and embryos.
How Does ART Cryopreservation Work?
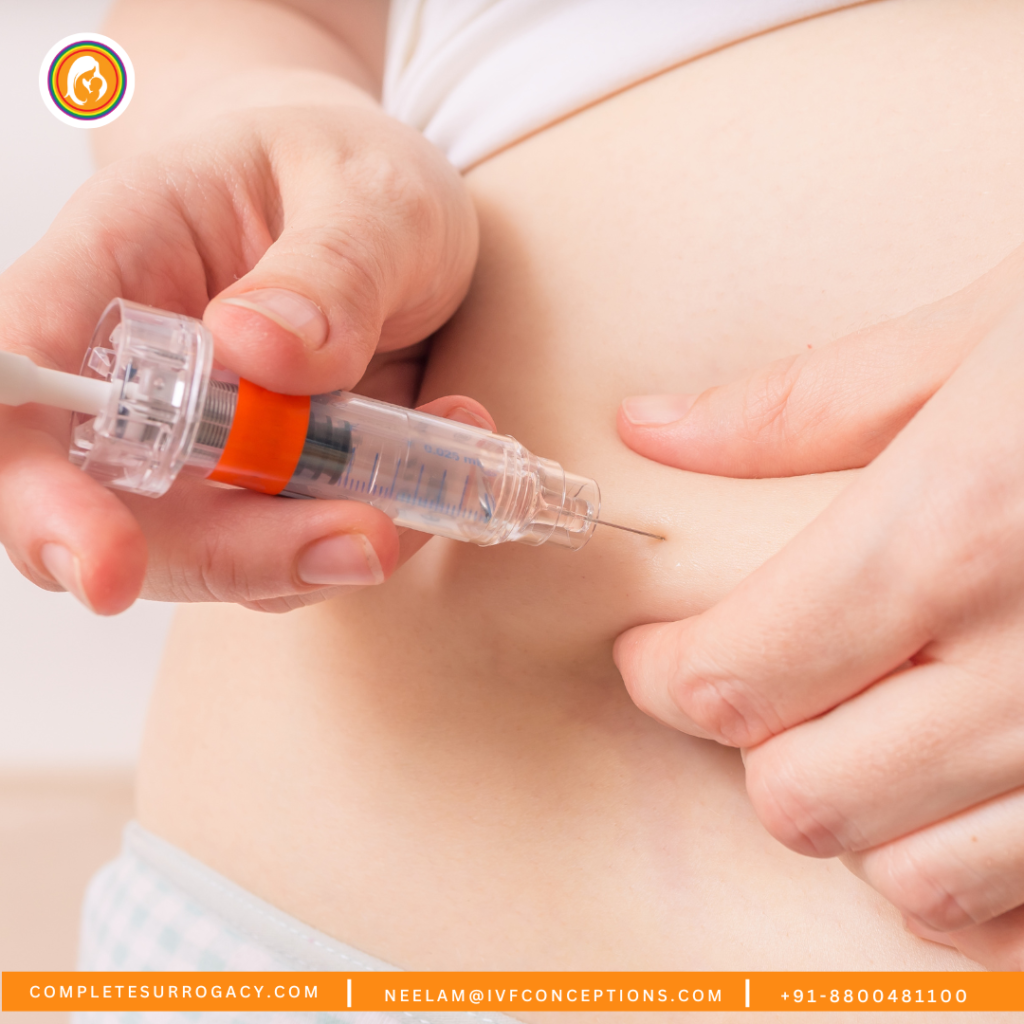
The Cryopreservation Process
| Step | Process | Details |
| Step 1: Collection | Sperm Collection | – Usually obtained through ejaculation. – Can also be retrieved directly from the testes if necessary. |
| Egg Retrieval | – Involves ovarian stimulation to produce multiple eggs. – Eggs are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure. | |
| Step 2: Freezing | Sperm Freezing | – Sperm is mixed with a cryoprotectant to protect cells during freezing. – Slowly cooled and then stored in liquid nitrogen. |
| Egg and Embryo Freezing | – Eggs and embryos are mixed with a cryoprotectant. – Rapidly cooled through a process called vitrification to prevent ice crystal formation. | |
| Step 3: Storage | Long-Term Storage | – Stored in liquid nitrogen tanks at temperatures around -196°C. – Can be stored for many years without significant loss of viability. |
| Thawing and Usage | Thawing Process | – Thawing must be done gradually to prevent damage. – Cryoprotectant is carefully removed. |
| Viability Check | – Sperm, eggs, or embryos are assessed for viability post-thawing. |
The process of ART cryopreservation can be broken down into several critical steps:
- Collection:
- Sperm Collection: Typically obtained through ejaculation or, in some cases, directly from the testes via surgical retrieval.
- Egg Retrieval: Involves ovarian stimulation followed by the retrieval of eggs through a minor surgical procedure.
- Embryo Creation: Eggs are fertilized with sperm in a lab setting to create embryos, which can be frozen for future use.
- Freezing:
- Sperm Freezing: Sperm is mixed with a cryoprotectant and gradually cooled before being stored in liquid nitrogen.
- Egg and Embryo Freezing: Eggs and embryos are vitrified, a process that rapidly cools them to prevent ice crystal formation.
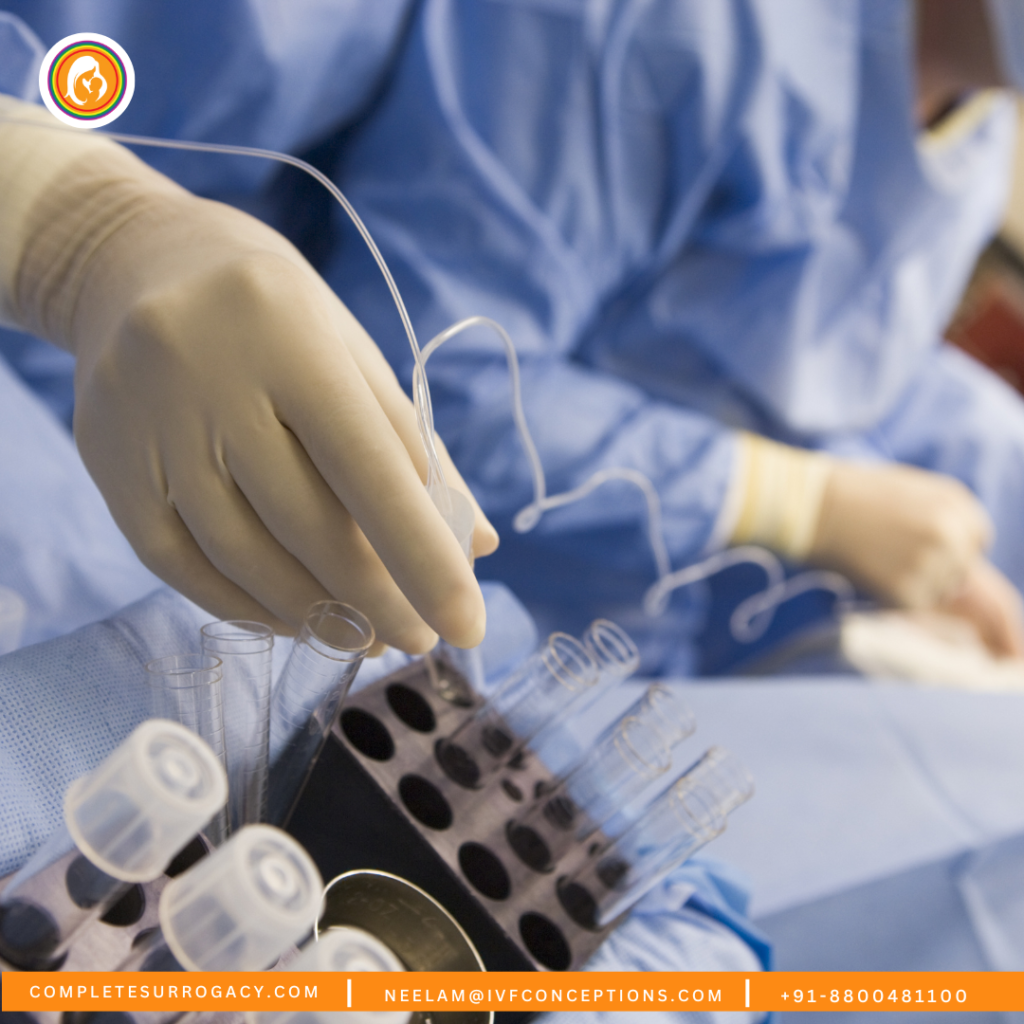
- Storage:
- Long-Term Storage: Frozen sperm, eggs, and embryos are stored in liquid nitrogen tanks at -196°C. These samples can remain viable for years, offering flexibility in reproductive planning.
- Thawing and Usage:
- Thawing Process: The samples are carefully thawed to minimize damage, and cryoprotectants are removed gradually.
- Usage:
- Sperm: Used for intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF).
- Eggs: Fertilized through IVF to create embryos.
- Embryos: Transferred to the uterus during an IVF cycle.
Benefits of ART Cryopreservation
ART cryopreservation offers numerous benefits, making it a valuable tool in fertility preservation:
- Flexibility: Allows individuals and couples to delay pregnancy until they are ready, whether for personal, career, or health reasons.
- Increased Success Rates: Cryopreservation provides multiple opportunities for successful implantation and pregnancy, particularly when using high-quality embryos.
- Fertility Preservation: Essential for individuals undergoing treatments like chemotherapy that may affect fertility. By freezing sperm, eggs, or embryos, they can preserve their chances of having biological children in the future.
Challenges and Limitations
While cryopreservation is a powerful tool, it is not without challenges:
- Potential for Cell Damage: The freezing and thawing processes can damage cells, reducing their viability. Proper use of cryoprotectants and controlled freezing rates are critical to minimizing this risk.
- Survival Rates: Not all cells survive the cryopreservation process, and success rates can vary based on the quality of the samples and individual circumstances.
- Legal and Ethical Issues: The regulation of cryopreserved samples varies by country, and ethical concerns, particularly around the storage and usage of embryos, are ongoing.
Applications of Cryopreservation in ART
Cryopreservation has broad applications in ART, including:
- IVF Cycles: Embryos from an IVF cycle can be frozen for future attempts, increasing the chances of a successful pregnancy without the need for repeated ovarian stimulation.
- Egg and Sperm Banking: Individuals can preserve their fertility by freezing eggs or sperm, which can be used later when they are ready to start a family.
- Oncofertility: Patients undergoing treatments that may impair fertility, such as chemotherapy, can freeze eggs, sperm, or embryos before treatment.
The Future of Cryopreservation
The field of cryopreservation is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research aimed at improving techniques and outcomes:
- Advanced Cryoprotectants: New cryoprotectants are being developed to enhance cell survival rates during the freezing and thawing processes.
- Cryogenics and Regenerative Medicine: Researchers are exploring the potential of cryopreservation in regenerative medicine, including the preservation of tissues and organs for transplantation.
More Resources to Read:
Surrogacy Guide for Surrogate Mothers
Surrogacy Guide for Intended Parents
How does the surrogacy process work
Conclusion
Cryopreservation is a cornerstone of modern reproductive medicine, offering a pathway for individuals and couples to preserve their fertility and plan their families on their terms. As technology advances, the possibilities for cryopreservation continue to expand, making it an increasingly vital component of ART. Understanding this process can empower intended parents to make informed decisions about their reproductive futures.
If you’d like to learn more about IVF, Egg Donation, or surrogacy services globally, check out the rest of our website at Complete Surrogacy Agency. We offer legally secure and affordable surrogacy consulting services for FREE.
Complete Surrogacy: Your Trusted Partner in International Surrogacy
At Complete Surrogacy, we have over 15 years of experience in international surrogacy, guiding 4,000+ intended parents worldwide. We provide safe, ethical, and affordable surrogacy solutions for single parents, LGBTQ+ couples, and heterosexual couples.
As members of EFS and ESHRE, we adhere to the highest ethical and professional standards. Our expert team is committed to providing accurate, compassionate, and transparent guidance, ensuring a legally secure and smooth journey to parenthood.
Let us help you build your family with trust, care, and integrity.
Get in touch for one FREE Surrogacy Consultancy!

FAQs for ART Cryopreservation
1. What is cryopreservation in ART?
Cryopreservation in ART refers to the freezing and storage of reproductive cells—sperm, eggs, and embryos—at ultra-low temperatures to preserve their viability for future use.
2. How does vitrification differ from traditional freezing?
Vitrification is a rapid freezing technique that prevents ice crystal formation, reducing the risk of cell damage compared to traditional slow-freezing methods.
3. What are the risks associated with cryopreservation?
Risks include potential cell damage during the freezing and thawing processes, as well as ethical and legal concerns regarding the storage and use of cryopreserved embryos.
4. How long can sperm, eggs, or embryos be stored?
Cryopreserved samples can be stored for many years without significant loss of viability, allowing for future use when the individual or couple is ready.
5. What are the future prospects of cryopreservation in medicine?
The future of cryopreservation holds promise in regenerative medicine, with ongoing research focused on improving techniques for preserving tissues and organs for transplantation.

Author Bio: Neelam Chhagani is an International Surrogacy Expert with 15 years of experience in the fertility and surrogacy domain. As the founder of IVF Conceptions and Complete Surrogacy, she has guided over 4,000 intended parents worldwide on their surrogacy journey to parenthood. Recognized as a trusted authority, she specializes in holistic infertility solutions and third-party reproduction consulting.
Holding an MA in Counselling Psychology and a PGD in Mental Health, Neelam is a proud member of the European Fertility Society (EFS) and the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE). She is also a leading surrogacy blogger, providing valuable insights into ethical and practical surrogacy solutions.
Since 2010, committed to supporting ALL family types, Neelam has been passionate about helping intended parents grow their families with compassion, integrity, and a focus on secure and affordable surrogacy options Globally.
Learn more about Neelam:
https://www.ivfconceptions.com/neelam-chhagani-surrogacy-consultant/
https://www.linkedin.com/in/neelam-chhagani-92892229/














I was introduced to Neelam by a friend who worked with Neelam for surrogacy. Neelam is absolutely wonderful. I am a single male and the journey to fatherhood is not that easy. Neelam connected me to a program ideal for my circumstances. She was with me throughout the pregnancy providing advice and guidance along the way. I am so grateful I found her and am thrilled today that I have a beautiful daughter. I highly recommend Neelam to anyone who is on a journey to become a parent. Having a child has changed my world for the better. I wish others success with their own journey and recommend you connect with Neelam to find a path that is best for you.
SA (USA)